Osteochondrosis (degenerative intervertebral disc disease) in the lumbar spine or in the lower back is caused by involving the intervertebral discs, which lead to pain in the lower back area.
Intervertebral discs are robust, fibrous structures that act as ligaments between the vertebrae, absorb bumps and ensure the shock absorption of the spine.The intervertebral discs are flexible, but strong enough to enable movements such as the forward, reverse or sideways bending of the upper body.
Despite the name, osteochondrosis is not considered a real illness and the symptoms are usually not worse over time.Like all structures of the body, intervertebral discs decrease with age, and in the context of the involvement process, interglace regeneration develops in all people.
A characteristic feature of osteochondrosis is a gradual decline in symptoms when the spine begins to stabilize.The treatment of a degenerative intervertebral disc disease of the lumbar spine focuses on pain relief, the stabilization of the spine and the improvement or maintenance of mobility.
Symptoms
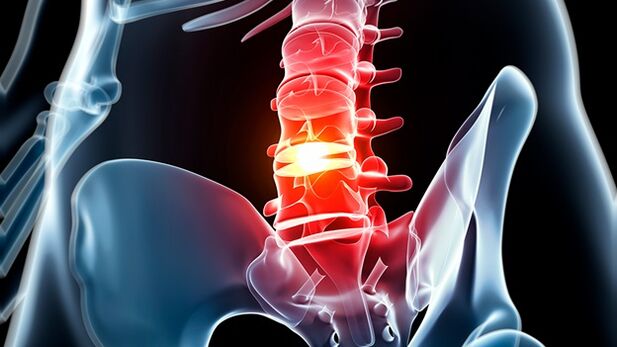
Most manifestations of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are mild, persistent back pain that increases from time to time over several days or longer.
The symptoms can vary, but most often are:
- Moderate, persistent pain in the lower back.Pain in the area of the damaged intervertebral disc is the most common symptom of intervertebral vein regeneration.The pain can radiate into the buttocks, the groin area and the thighs.This pain usually feels dull and can be from light to severe intensity.
- Periodic acute pain episodes.Back pain can worsen for a few days or weeks and then take a milder extent again.When the spine degenerates, pain pacifiers occur, which decrease with the gradual stabilization of the spine.Excess pain can suddenly occur and pain often leads to limited mobility.
- Local pain.The area of the lower back that surrounds the degenerated intervertebral disc can be sensitive when touched.Local pain arises from inflammation and muscle tension in the area of the intervertebral disc damaged by degeneration.
- Pain in the leg.Neurological symptoms, including deafness, weakness or sharp, shoot pain in the buttocks, the hips and / or back of the leg, can feel if the height of the pane is significantly reduced and the conditions for compression of the nerve root result.The pain in the legs with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine usually does not fall under their knees.
- A feeling of sudden weakness or instability can occur with a significant weakening of the disc, and the patient creates that the lower back executes its functions incompletely.
In addition, the pain can intensify or reduce if some movements or certain poses are carried out, such as:B.:
- Pain in the seat. Sitting over long periods of time often causes increased pain and stiffness in the lower back and decreases after the formation or change in the position.
- Increase pain by tilting or rotating.Rotating the spine and tilting it forward, back or side can cause intense pain in the damaged disc.
- Reduce pain when walking or changing the position.When the spine changes the position, the pressure on the windows removes or is redistributed by slices to muscles and joints.Frequent positions, alternating standing and sitting as well as short walks can help reduce the stiffness and minimize the pain.
The degeneration of the hard disk should not cause symptoms of a intestinal dysfunction / bladder, fever with back pain, inexplicable and fast weight loss or intensive abdominal pain.These symptoms indicate more serious diseases and often require operational methods of treatment.
Associated symptoms
In the case of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms associated with disc degeneration can occur in addition to the pain in the lower back.For example:
- Proteins contained in the pane can cause significant inflammation if they come into contact with the surrounding vertebral structures, and this inflammation can lead to cramps of the lower back muscles and to radial pain with radiation in the hips and on the back surface of the lower extremities (also called Ishias).
- The degeneration of the lumbar can contribute to the development of lumbar stenosis and / or lumbar osteoarthritis and other diseases in the lower back.
- A degenerated disc can also lead to the appearance of a hernia of the lumbar intervertebral disc.Neurological symptoms with a disc can be acute and intense.
- The symptoms caused by the degeneration of the pane in the lumbar spine can vary greatly, depending on how quickly or completely the disc has experienced degeneration and how it affects the surrounding spine structures.
- Pain in osteochondrosis is usually caused by the deformation of the muscles that support the spine and the inflammation around the structures near the intervertebral disc.
The causes of the osteochondose of the lumbar spine
Osteochondrosis occurs due to old age and diseases of the disc structure, and the degeneration process can accelerate due to injuries, general condition, health and lifestyle and possibly a genetic assessment for the development of pathological processes in the musculoskeletal system.
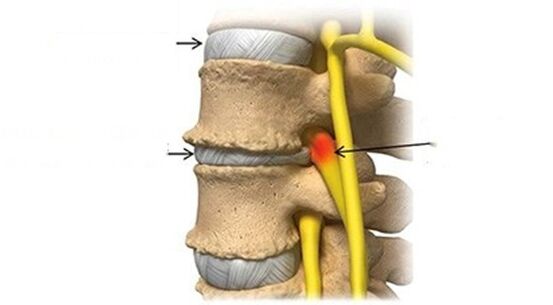
Osteochondrosis rarely begins with a serious injury, such as:B. a car accident.It is more likely that the initiation of degenerative processes is associated with a disc injury with low energy.
Right pain in connection with lumbar osteochondrosis is usually generated by one or more pathological processes:
- Inflammation, proteins from the disc are irritated by the surrounding nerves - both small nerves in the window itself and possibly large nerves that go on the feet (sciatic nerve).
- The abnormal instability of the micros, when the outer rings of the disc, which are referred to as a fibrous ring, can wear out and no performance vectors on the spine can effectively absorb, which leads to movements along the spine.
- The pain in the osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine ultimately decreases over a long period of time and not worse.This pain relief occurs, since the disc, completely damaged by degeneration, no longer has inflammatory proteins (which can cause pain) and the sleeping plate merges into a stable position and removes microt movements that cause pain.
Risk factors
Lifestyle factors that influence the general state of health can influence the intervertebral discs between vertebrae.The risk factors of a degenerative disc disease (osteochondrosis) include:
- Family history of back pain or skeletal and muscle disorders
- Excessive load on the floor of the back due to sports or the type of work
- Long static loads on the windows due to longer seats and / or poor posture
- Lack of disc support due to weak back muscles
- obesity
- Smoking or any form of nicotine consumption
The degeneration of the hard drive is part of the aging of the body, but not all people develop pain or special symptoms.The symptoms tend to occur with instability, muscle tension and possibly irritation of the nerve roots.
Diagnosis
- The anamnesis of the disease includes a detailed examination of the patient's symptoms, its intensity and the ratio of pain to the loads or position of the body.Information about regular physical activity, sleeping habits and past injuries is also required.
- A physical examination is necessary to examine the area of movement and the condition of the sore muscles.The presence of painful areas on palpation or physical anomalies is also determined.In addition, neurological tests are carried out to determine a neurological deficit.
- The above diagnostic methods are usually sufficient for the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, but a precise diagnosis requires the use of visualization methods.
- CT
- Radiography
- MSCT
- KNOCK
- MRI - This diagnostic method allows you to clarify the degree of degeneration, the presence of fractures, hernias of stenosis discs.Often, an MRI study is required in preparation for surgical treatment to accurately determine the location of the degenerated disc and plan the operation.
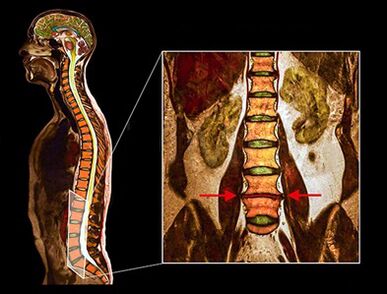
Studies have shown that the results of the MRI with moderate or significant disceneration are found when scanning patients with severe pain and minimal or lack of pain.In addition, many painful conditions may not appear on an MRI.For this reason, the diagnosis cannot be made exclusively on the basis of the results of the visualization, and checking the diagnosis is only possible due to the entirety of all clinical and instrumental examination methods.
Treatment
The initial methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine and pain manifestations usually include the following combinations:
- Over complex painkillers You can reduce inflammation, which contributes to complaints, stiffness and irritation of nerve roots.
- Prescription pain relievers.In the event of severe pain, muscle relaxants or narcotics pain can be prescribed.These drugs are usually used to treat intensive, acute pain that is expected to take more than a few days or weeks.These drugs can cause addiction and cause serious side effects so that they should be used with caution.
- Heat and ice cream.The use of heat in the lower back improves blood circulation, which reduces muscle cramps and tensions and improves mobility.Ice packaging can reduce inflammation and alleviate moderate pain.It is useful to use heat from physical exercises to relax the muscles and use ice cream after physical activity to minimize inflammation.
- Manual therapy. The manipulation is carried out by a specialist, is a popular method to control the pain in the lower back.Practitioning doctors, manual therapists, use their hands to influence different areas of the body to reduce the tensions in muscles and joints.It was found that manipulations are an effective measure of temporary reduction in pain and in some cases as effective as drug therapy.
- massage.Exposition by massage methods can reduce the tension and cramps in the muscles of the lower back, reduce the pressure on the spine and relieve pain.In addition, the therapeutic massage can improve blood circulation and ensure the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to tense muscles.
- Epidural injections of steroids.The introduction of the steroid into the room that surrounds the spine can reduce pain impulses and inflammation.The injection of steroid can be used in combination with the physiotherapy program to relieve pain during physical exercises and rehabilitation.As a rule, the epidural injection of steroids enables the pain of several weeks to a year.
In many cases, a combination of treatment methods is required for effective anesthesia.The process of experiment and error is usually necessary to choose treatment that turns out to be most effective.
Long bed rest is not recommended, and as a rule, immobilization is possible for a short time with severe pain, since the lack of physical activity can lead to a weakening of the muscles and normal support for the spine.
Training therapy and change in activity

In order to maintain healthy mobility of the spine, physical exercises are required.An effective training program for the lumbar spine should include:
- Exercises for stretching the muscles of the lower back, hips and pelvis as well as the muscles of the Harmestring.The seal of these muscles increases the pressure on the lumbar spine and contributes to the development of pain in the lower back.
- Power exercises on the muscles of the lower back and abdomen allow you to maintain good posture, and it is better to maintain the spine.The program of exercises to strengthen muscles may include an individual exercise therapy program, dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine, Tai Chi, Pilates or others.
- Aerobic exercises with a low level of stress that increase the frequency of heart contractions, improve blood circulation and provide nutrients and oxygen, which is necessary to restore body tissue.For example, it can work, swim and water aerobic.
Programs of physical exercises are usually adapted depending on the general state of health, the severity of pain and personal preferences.
In addition, small adjustments to daily activity (modification of the lifestyle) can effectively increase the pain.For example, putting on a corset when lifting weights or avoiding twisting when lifting weights can prevent increased pain due to excessive loads on the windows.The use of an ergonomic chair and an orthopedic mattress can also improve the posture and reduce the load of the discs.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of osteochondose of the lumbar spine is necessary in cases where conservative treatment was inefficient for 6 months.The surgical treatment of osteochondrosis is always selective, which means that the patient himself decides whether the operation should undergo or not.
It is recommended to take all factors into account before you choose osteochondrosis surgery, including the duration of the recovery phase, the treatment of pain during recovery and rehabilitation of the spine.
The fusions of the vertebrae
The standard surgical treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is a merger surgery in which two vertebrae are spent together.The purpose of the mergers (spondylodeza) is to reduce the pain and to eliminate the instability in the motor segment of the spine.
All spinal fusion operations are as follows:
- The damaged disc is completely removed from the intervertebral disc (discoctomy).
- The stabilization is carried out using a bone transplant and / or the tools (implants, plates, sticks and / or screws).
- Then the vertebrae merge and form a solid, motionless structure.Fights occur within a few months after the procedure and not during the operation itself.
After operation, wearing a corset and taking analgesics are prescribed.The exercises are very carefully connected, whereby the individual characteristics of the patient and the degree of tissue regeneration are taken into account.The complete recovery after the merger can take up to a year for the vertebrae grow together.
Surgical replacement of an artificial disc
Replacing the damaged hard drive with an artificial implant has been developed in recent years as an alternative to fusions.The disk replacement procedure consists in completely eliminating the disk damaged by degeneration (discoctomy), restoring the disk space to the natural height and implanting the artificial disk.
This process is intended to maintain the movement in the spine, similar to natural movements, which reduces the probability of increasing pressure on neighboring spinal segments (rather frequent complication of the spine fusion).
Recovery from hard drive replacement typically takes up to 6 months.
























